Feb 24th 2017
What Is The Endocannabinoid System?
THE HUMAN ENDOCANNABINOID SYSTEM IS MARVELOUS
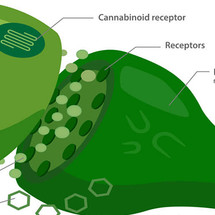
Discovered in the 20th century, our Endocannabinoid System (ECS) consists of numerous cannabinoid receptors that are endogenous to our brains.
They play a pivotal role in many of our physiological processes such as mood, memory, pain modulation, appetite. Plus it has been shown to have positive effects as an anti-inflammatory aid along with other immune system responses.
The recent identification of cannabinoid receptors has triggered an exponential growth of studies. These studies targeted explored the endocannabinoid system and its regulatory functions in health and disease.
This system has been associated in a growing number of physiological functions. This includes, but is not limited to, both the central and peripheral nervous systems along with peripheral organs.
THE CB1 & CB2 RECEPTORS
CB1 Receptors: Are primarily found in the brain and central nervous system. To some lesser extent, it's also found in other tissues in the human body.
CB2 Receptors: These receptors are primarily found in the peripheral organs especially cells associated with the immune system.
It should be noted that CBD does not directly fit CB1 or CB2 receptors but has powerful indirect effects still being studied.
CANNABINOIDS, YOUR BODY AND MIND
The endocannabinoid system help cells communicate each other and with tissues, organs, and larger systems within the body. Cannabinoids can influence a person’s relationship with the external environment in addition to regulating our internal and cellular homeostasis.
As research has progressed, there is now evidence to support the ECS (Endocannabinoid System) as a bridge between body and mind. You can see what parts of the brain are most affected as well as which functions are associate with that part of the brain.